Organizational Structure
Organizational StructureA social enterprise may be structured as a department, program or profit center within a nonprofit and lack legal definition from its parent organization. It may also be a subsidiary of its nonprofit parent, registered either as a for-profit or nonprofit. Many organizations use a mix of different structures simultaneously.
The following diagrams illustrate the social enterprise structure vis-à-vis its relationship to the parent organization.
Structured Internally
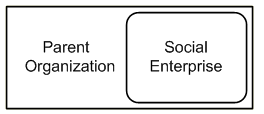 Social enterprise is structured as a department or profit center within the parent organization. The social enterprise may (or may not) physically share space with the parent. From a legal, financial, management, and governance perspective the enterprise is internal to its nonprofit parent. Systems, back office, staff, and leadership are integrated.
Social enterprise is structured as a department or profit center within the parent organization. The social enterprise may (or may not) physically share space with the parent. From a legal, financial, management, and governance perspective the enterprise is internal to its nonprofit parent. Systems, back office, staff, and leadership are integrated.
Any of the operational models can be structured internally within the parent organization; however, embedded and integrated social enterprises are the most common forms using this structure.
Structured as a Separate Entity
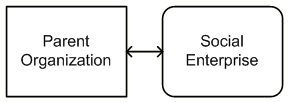 Social enterprise is structured as a separate legal entity, either a for-profit or a nonprofit. In this case, the social enterprise may or may not physically share space with the parent. From a legal, financial, management, and governance perspective the enterprise is external to its nonprofit parent. If staff, overhead, or back office is shared, this is done so on a formal (contractual) basis as a business relationship. .
Social enterprise is structured as a separate legal entity, either a for-profit or a nonprofit. In this case, the social enterprise may or may not physically share space with the parent. From a legal, financial, management, and governance perspective the enterprise is external to its nonprofit parent. If staff, overhead, or back office is shared, this is done so on a formal (contractual) basis as a business relationship. .
Any of the operational models can be structured as a separate entity from the parent organization; however, integrated and external social enterprises are the most common forms using this structure.
Structured as the Same Entity
 Social enterprise is the same entity as the parent organization, meaning functionally that there is NO parent or host organization, rather the social enterprise is the only activity of the organization. There is no delineation between program, administrative and infrastructure aspects indicating the existence of two or more types of activities. This type of social enterprise may evolve into one of the other structures by adding new enterprises or social programs.
Social enterprise is the same entity as the parent organization, meaning functionally that there is NO parent or host organization, rather the social enterprise is the only activity of the organization. There is no delineation between program, administrative and infrastructure aspects indicating the existence of two or more types of activities. This type of social enterprise may evolve into one of the other structures by adding new enterprises or social programs.
Embedded social enterprises are the most common form using this structure.